Supercharge your Application with Real-time Low-Latency Edge Computing

We’re kicking off our blog series with some exciting news! We are collaborating with our friends at Redpanda to help applications deliver low-latency real-time experience to their users.
How does it work?
WebSocket connections are crucial in building and delivering real-time applications. YoMo leverages edge-nodes on a global scale and connects to the cloud by QUIC protocol. As a result, applications can handle persistent WebSocket connections closer to the user, and provide a richer low-latency real-time experience. The processed data is streamed to Redpanda — a high performance framework guaranteeing data safety.
About Redpanda
Redpanda, as Vectorized put it, is a Kafka API compatible streaming platform for mission-critical workloads. It is lightweight, optimized for performance, and requires no ZooKeeper management.
About YoMo
YoMo is an open-source Streaming Serverless Framework for building Low-latency Edge Computing applications. Built atop QUIC Transport Protocol and Functional Reactive Programming interface. makes real-time data processing reliable, secure, and easy.
Why YoMo?
- As of this writing, we are the only platform using QUIC transport protocol that is specifically optimized for edge computing.
- You handle the business logic, we take care of everything else.
- Handling raw data streams can be intimidating. YoMo simplifies the process by introducing ReactiveX, which is considered one of the best ways to handle time-sensitive data streams.
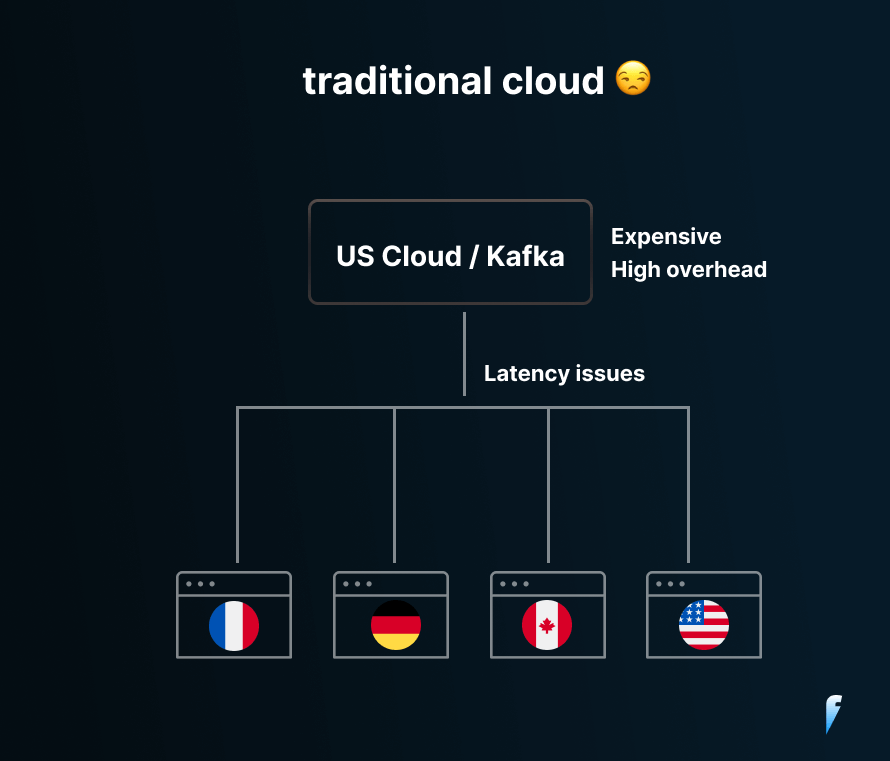
Traditional Cloud-Centric architecture:
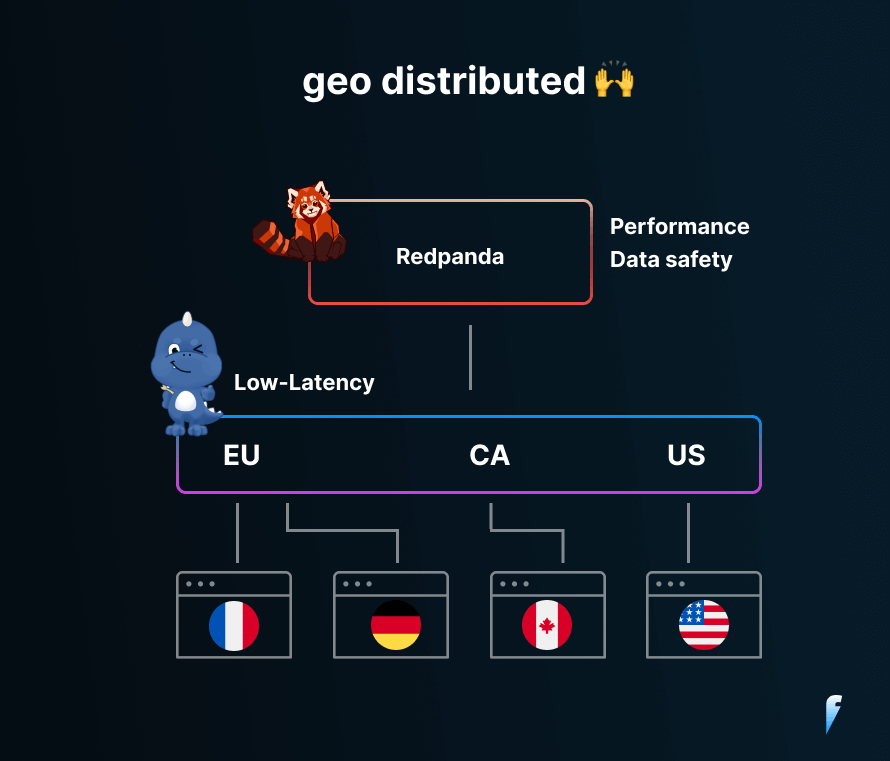
State-of-the-art Geo-Distributed architecture:
Let’s get started!
1) Install RedPanda: Please visit Redpanda - Getting Started and enable Pandaproxy after installation.
In this example, we will use HTTP REST API in Pandaproxy to produce the messages.
2) Install YoMo: Please visit YoMo - Getting Started.
Now that you have installed both services, there are 5 easy steps to follow:
Step 1: Create a topic in Redpanda
We will call it "yomo-test":
rpk topic create yomo-test
Step 2: Create your serverless app
For further details please refer to YoMo - GitHub.
Step 3: Copy the following code to your serverless app
package main
import (
"bytes"
"context"
"encoding/json"
"errors"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
y3 "github.com/yomorun/y3-codec-golang"
"github.com/yomorun/yomo/pkg/rx"
)
// noiseDataKey represents the Tag of a Y3 encoded data packet.
const actionDataKey = 0x10
// batchSize is the amount of data that will be inserted into Redpanda in batch.
const batchSize = 100
// bufferMilliseconds is the time in milliseconds that the data will be buffered and inserted into Redpanda in batch.
const bufferMilliseconds = 3e3
var (
pandaProxyURL = "" // Redpanda Proxy URL.
topic = "" // Topic name.
)
func init() {
pandaProxyURL = os.Getenv("PANDAPROXY_URL")
if pandaProxyURL == "" {
pandaProxyURL = "http://localhost:8082"
}
topic = os.Getenv("REDPANDA_TOPIC")
if topic == "" {
topic = "yomo-test"
}
}
// noiseData represents the structure of data.
type actionData struct {
Noise float32 `y3:"0x11" json:"movements"`
Time int64 `y3:"0x12" json:"timestamp"`
From string `y3:"0x13" json:"from"`
}
// postData represents the structure of records that will be posted to Redpanda.
type postData struct {
Records []postDataItem `json:"records"`
}
// postDataItem represents the structure of data item.
type postDataItem struct {
Value interface{} `json:"value"`
Partition int `json:"partition"`
}
// getPostBody gets the body of HTTP POST to Redpanda Proxy.
func getPostBody(data []interface{}) ([]byte, error) {
items := make([]postDataItem, len((data)))
for i, act := range data {
items[i] = postDataItem{
Value: act,
Partition: 0,
}
}
return json.Marshal(postData{
Records: items,
})
}
// write data to Redpanda Proxy in batch via RESTful API.
var produce = func(_ context.Context, v interface{}) (interface{}, error) {
data, ok := v.([]interface{})
if !ok {
return nil, errors.New("v is not a slice")
}
postBody, err := getPostBody(data)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// post data to Redpanda
resp, err := http.Post(fmt.Sprintf("%s/topics/%s", pandaProxyURL, topic), "application/vnd.kafka.binary.v2+json", bytes.NewBuffer(postBody))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
return nil, err
}
defer resp.Body.Close()
// read the response body
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalln(err)
return nil, err
}
// print the response
log.Printf(string(body))
return fmt.Sprintf("⚡️ write %d items to redpanda successfully", len(data)), nil
}
// decode from Y3 codec
var decode = func(v []byte) (interface{}, error) {
var mold actionData
// decode bytes by Y3 Codec.
err := y3.ToObject(v, &mold)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// return the JSON encoding for insertion in Redpanda.
b, err := json.Marshal(mold)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return b, nil
}
// Handler will handle data in Rx way
func Handler(rxstream rx.RxStream) rx.RxStream {
stream := rxstream.
Subscribe(actionDataKey).
OnObserve(decode).
BufferWithTimeOrCount(bufferMilliseconds, batchSize).
Map(produce).
StdOut().
Encode(actionDataKey)
return stream
}
Step 4: Run your serverless app in dev mode
PANDAPROXY_URL is the URL of PandaProxy in Redpanda.
$ PANDAPROXY_URL=http://127.0.0.1:8082 yomo dev
2021/03/18 14:13:13 Building the Serverless Function File...
2021/03/18 14:13:16 ✅ Listening on 0.0.0.0:4242
2021/03/18 14:13:19 {"offsets":[{"partition":0,"offset":113}]}
[StdOut]: ⚡️ write 10 items to redpanda successfully
2021/03/18 14:13:20 {"offsets":[{"partition":0,"offset":123}]}
[StdOut]: ⚡️ write 10 items to redpanda successfully
2021/03/18 14:13:21 {"offsets":[{"partition":0,"offset":133}]}
[StdOut]: ⚡️ write 10 items to redpanda successfully
2021/03/18 14:13:22 {"offsets":[{"partition":0,"offset":143}]}
[StdOut]: ⚡️ write 10 items to redpanda successfully
Step 5: Consume the messages in Redpanda
rpk topic consume yomo-test
That’s it!
You should be able to see the following messages:
{
"message": "{\"movements\":153.04851,\"timestamp\":1616048002511,\"from\":\"127.0.0.1\"}",
"partition": 0,
"offset": 150,
"timestamp": "2021-03-18T06:13:22.888Z"
}
{
"message": "{\"movements\":43.49945,\"timestamp\":1616048002611,\"from\":\"127.0.0.1\"}",
"partition": 0,
"offset": 151,
"timestamp": "2021-03-18T06:13:22.888Z"
}
{
"message": "{\"movements\":85.69591,\"timestamp\":1616048002711,\"from\":\"127.0.0.1\"}",
"partition": 0,
"offset": 152,
"timestamp": "2021-03-18T06:13:22.888Z"
}
Stay tuned
This blog post covers WebSocket usage with YoMo and Redpanda in a broad view. A second part of this article showcasing a niche Virtual HQ use case is coming up, so stay tuned!
Have any questions? Join our channels
YoMo Discord: Click here to join
Redpanda Slack: Click here to join
